Rheumatology Services
Rheumatology Services
We Take Care Of Your Health
We offer the best healthcare for you and your family.

RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)
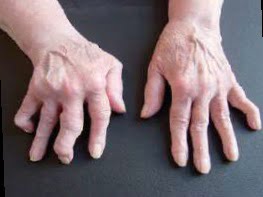
RA is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The immune system attacks healthy cells in the body by mistake, causing inflammation (painful swelling), commonly hands, wrists, knees and feet.
Symptoms
Joint pain, swelling and stiffness that lasts for six (6) weeks or longer. Usually involves both hands and feet.
Causes
The causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis are unknown. But are believed to be genes, environment, and sex hormone.
Treatment Includes
● Steroids
● NSAIDS (Anti-inflammatory medications).
● DMARDS (Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs)
– eg. Methotrexate, Hydroxychloroquine, Sulphasalazine, Leflunomide
● tsDMARDS (Baricitinib, Tofacitinib, Upadacitinib)
● Biologics (Subcutaneous Injections Anti-TNF/IL-6/anti-CD20)
More Information
● Joint damage/Deformity – Prosthesis/Surgery.
● Occupational Therapy & Physioterapy.
● Diet & Lifestyle Changes.
Rheumatoid Hands

PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS (PsA)
A form of Arthritis that affects some people who have “Psoriasis” – A skin condition that causes red skin patches with silvery scales.
Symptoms
Swollen Fingers & Toes (Sausage-like digits), Foot Pain (Heel & Sole of foot), Lower Back Pain, Nail Changes (Pitting/Crumbling).
Causes
Unknown, possibly related to Genetic/Immune Cause
Risk Factor
Family history of psoriasis
Treatment Includes
● Topical Steroids + Salicylic Ointment
● DMARDS (Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs)
– eg. Methotrexate, Sulphasalazine, Leflunomide
● Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKi)
● Biologics (Subcutaneous Injections anti-IL 17, anti-TNF, IL-12/23)
More Information
● Combined management with the dermatologist is preferred.
● Physiotherapy & Occupational Therapy.
● Joint damage/Deformity – Prosthesis/Surgery.

GOUTY ARTHRITIS
Gout is a form of crystal inflammatory arthritis.
Symptoms
Sudden painful joints with swelling , usually affects the big toe causing difficulty to walk & tophi formation.
Causes
Hyperuricemia – Too much uric acid in the body causes uric acid crystals to build up in joints, fluids and tissues within the body.
Treatment - Acute & Chronic
● Acute : Colchicine, NSAIDs , Steroids, Ice Compression, Rest the joint.
● Chronic :
– Frequent attacks more than 2 times per year will need urate lowering therapy. Eg. Allopurinol, Febuxostat, Probenecid acid, Benzbromarone, Dietary restrictions.
*Aim to keep Serum Uric Acid Level < 360 Micromole/L.
● Low Purine Diet : reduce red meat, sweet drinks rich in fructose, anchovies, sardine, mackerel, tuna, internal organs (eg. liver, lungs, intestines).
● Increase plain water intake – 2-3 litre per day.

SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE)
This is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs.
Symptoms
SLE patients may experience a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, skin rashes, oral ulcers, fevers, joint pain, facial puffiness & leg swelling.
Causes
The causes of SLE are linked to environmental, genetic, and hormonal factors.
Treatment
There is NO CURE for lupus. However, early diagnosis and effective treatment and medications can help improve quality of life in SLE patients.
Medications
● Steroids
● Hydroxychloroquine
● Azathioprine, Methotrexate, Mycophenolate Mofetil, Cyclosporin
● Biologics (Belimumab, Anifrolumab)
OSTEOPOROSIS
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that develops when bone mineral density and bone mass decrease, or when the structure and strength of bone change. This can lead to a decrease in bone strength that increases the risk of fracture.
Symptoms
There are no symptoms of osteoporosis and can only be identified when one breaks hip bones, vertebrates in the spine, and wrist. Women are at more risk of getting osteoporosis than men.
Causes
Osteoporosis occurs when too much bone mass is lost and changes occur in the structure of bone tissue. It is also caused by risk factors such as:
● Modifiable risk factors: Vitamin D deficiency, obesity, general medical conditions and sedentary lifestyle.
● Non modifiable risk factors: sex, age, body size, race, family history and hormonal changes.
Treatment
- Medications to strengthen bones
- Surgery – to stabilise fracture
FIBROMYALGIA
What is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a chronic (long-lasting) disorder that causes pain and tenderness throughout the body, as well as fatigue and trouble sleeping.
Symptoms
Patients experience throbbing, aching, or burning pain throughout the body or multiple parts of the body such as arms, legs, head, chest, abdomen, back, and buttocks. The patient could also feel fatigue, tiredness and trouble sleeping (insomnia).
Causes
The causes of Fibromyalgia are unknown, but people with the disorder have heightened sensitivity to pain and it tends to run in families.
Treatment
Treatment typically involves a combination of medications, stretching exercises, psychological and behavioral therapy.
